Agrinio
Visit the guide

Alexandroupoli
Visit the guide
Amaliada
Visit the guide

Arta
Visit the guide

Athens
Visit the guide

Chalcis
Visit the guide
Chania
Visit the guide
Drama
Visit the guide

Florina
Visit the guide

Heraklion
Visit the guide

Ioannina
Visit the guide
Kalamata
Visit the guide
Karpenisi
Visit the guide

Katerini
Visit the guide

Kavala
Visit the guide

Komotini
Visit the guide

Kozani
Visit the guide

Lamia
Visit the guide

Larissa
Visit the guide
Mytilene
Visit the guide

Patras
Visit the guide

Preveza
Visit the guide

Pyrgos
Visit the guide
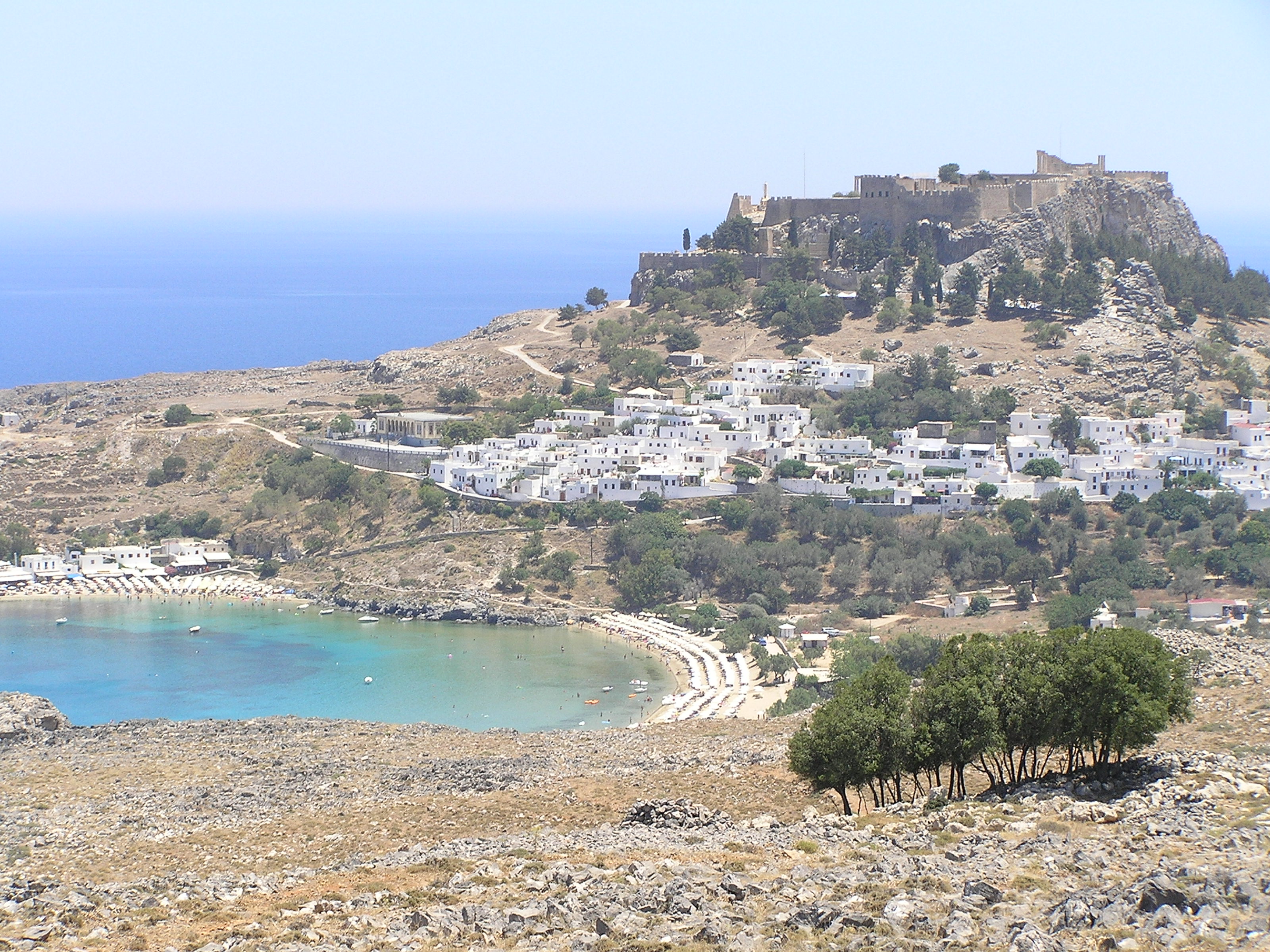

Rhodes
Visit the guide
Serres
Visit the guide

Thessaloniki
Visit the guide

Trikala
Visit the guide

Veria
Visit the guide

Volos
Visit the guide
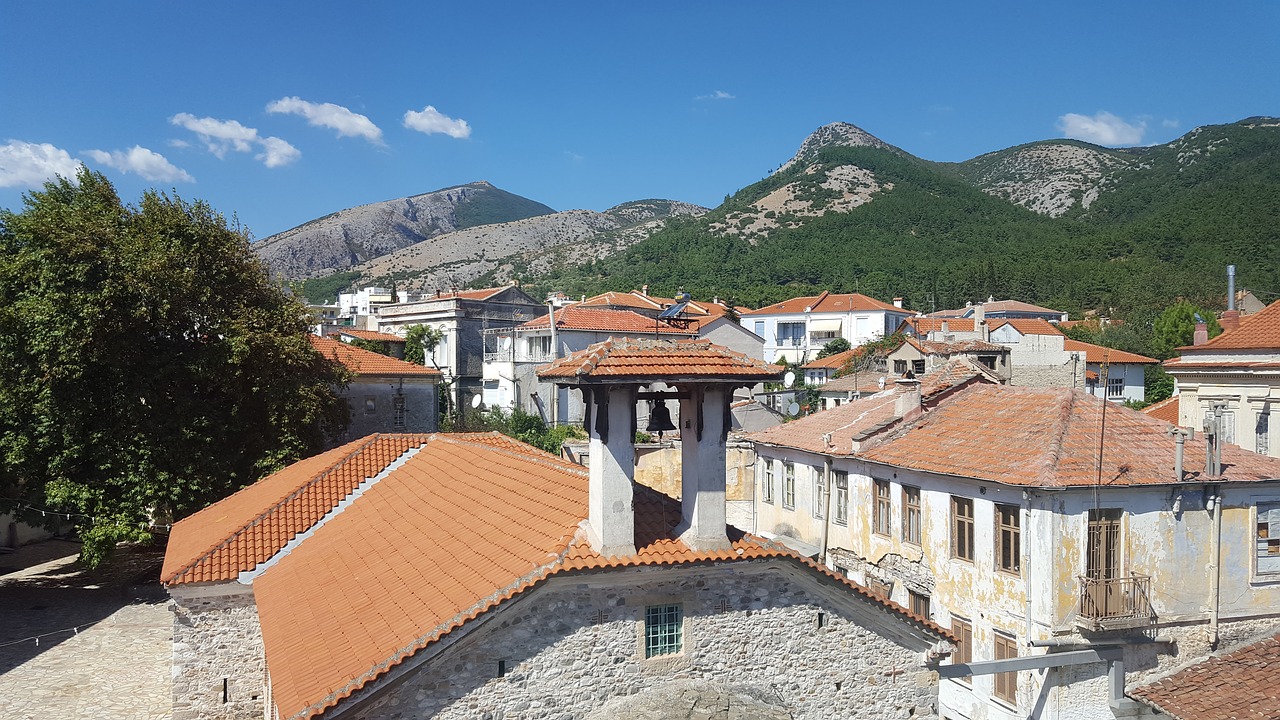

Xanthi
Visit the guide
festivites
Here are some of the major festivities or holidays in Greece, along with a brief explanation of their cultural traditions and how they are celebrated:
1. Easter: Easter is one of the most important religious holidays in Greece. Celebrated in April or May, it marks the resurrection of Christ and the end of Lent. Greeks attend church services throughout the week leading up to Easter Sunday. On Saturday night, people gather outside churches for the midnight Resurrection Mass, where fireworks light up the sky as the priest announces that Christ has risen. On Easter Sunday, families prepare a large feast featuring traditional dishes such as lamb, kokoretsi (spit-roasted lamb offal wrapped in intestine), and magiritsa (a soup made from lamb organs).
2. Independence Day: March 25th is Greece's Independence Day, commemorating the start of the Greek War of Independence against Ottoman rule. Military parades and schoolchildren's processions take place in Athens and other cities across Greece. Houses and buildings are decorated with Greek flags, and people wear blue and white, the colors of the Greek flag.
3. Apokries (Carnival): The Carnival season in Greece lasts for three weeks leading up to Clean Monday, which is the beginning of Lent. During this time, Greeks dress up in costumes, attend parties and parades, and eat traditional Carnival foods like loukoumades (honey-soaked doughnuts) and tiganites (pancakes). The biggest Carnival celebrations take place in the town of Patras, where there is a massive parade featuring floats and groups in elaborate costumes.
4. Name Days: In addition to birthdays, Greeks celebrate their name days, which are based on the Christian calendar of saints. On their name day, Greeks often host an open house for friends and family to come and celebrate with them. They serve sweets, drinks, and other treats and receive gifts and well-wishes.
5. Christmas: Christmas is another important religious holiday in Greece. On Christmas Eve, families attend church services and return home to eat a meal featuring traditional dishes like Christopsomo (a sweet bread with a cross on top) and roasted pork or lamb. On Christmas Day, it's customary to exchange gifts and visit friends and family.
These are just a few of the many festive occasions celebrated in Greece throughout the year, showcasing the country's rich cultural heritage and traditions.
seasons
In Greece, the tourist season is generally divided into three main periods:
1. High Season: Mid-June to August.
During this time, the weather is hot and sunny, and the beaches and tourist destinations are crowded. Prices for accommodations and activities are at their highest, so it's recommended to book in advance.
2. Shoulder Season: May to mid-June, and September to October.
This period offers milder temperatures than high season, fewer crowds, and lower prices. It's an ideal time to explore popular sites without long lines and enjoy outdoor activities.
3. Low Season: November to April.
The low season in Greece sees cooler temperatures and fewer tourists. While some islands and coastal areas may be closed during winter months, many cities and mainland destinations remain open and can offer better deals on accommodations and activities.
Overall, visitors should consider their preferences for weather, crowds, and budget when planning their trip to Greece.
visa
As an AI language model, I cannot provide real-time and up-to-date information on visa rules and costs for Greece or any other country. Visa requirements and costs can change frequently, and it's important to check with the relevant authorities, such as the Greek embassy or consulate in your home country, for the latest information. Additionally, visa requirements and costs may vary depending on various factors such as the purpose of the visit, the length of stay, and the applicant's nationality.
souvenirs
1. Olive oil - The price can range from 5-20 euros, depending on the brand and size of the bottle. You can buy it from any local supermarket or specialty food shop.
2. Honey - The price typically ranges from 5-15 euros for a jar of honey, depending on the type and quality. You can find it in local markets or specialized shops.
3. Greek wine - The prices vary widely depending on the winery and the vintage, but you can expect to pay between 10-30 euros for a bottle. You can buy it from the wineries themselves, as well as local supermarkets and wine shops.
4. Ceramic pottery - Prices vary depending on the type and size of the piece, but you can expect to pay between 10-50 euros for a small vase or plate. You can find it in local markets or souvenir shops.
5. Leather sandals - Prices vary depending on the style and quality, but you can expect to pay around 30-50 euros for a pair. You can find them in local markets or shoe shops.
6. Traditional Greek textiles - Prices vary depending on the item, but you can expect to pay around 20-50 euros for a scarf or tablecloth. You can find them in local markets or textile shops.
7. Feta cheese - The price can vary depending on the quality and freshness, but you can expect to pay around 5-10 euros per kilogram. You can buy it from any local supermarket or specialty food shop.
8. Greek coffee - The price can vary depending on the brand and package size, but you can expect to pay around 5-10 euros for a bag of coffee. You can find it in local markets or specialty food shops.
Note: Prices are subject to change and may vary depending on location and season.
If you have 1 week
Oh, Greece! Such a beautiful country full of history, culture and natural beauty. I have so many recommendations for your one week itinerary. Here are some places that you should definitely visit:
1. Athens: You must visit the capital city of Greece. Visit world-famous landmarks such as the Acropolis, the Parthenon and the Temple of Olympian Zeus. You can also enjoy traditional Greek food at Plaka, the oldest neighborhood in Athens.
2. Santorini: This is one of the most beautiful islands in Greece. The crystal-clear waters, the breathtaking views and the unique architecture will make you fall in love with this place. Don't forget to watch the sunset from Oia, it's a unique experience.
3. Meteora: This is a UNESCO World Heritage Site consisting of six monasteries built on top of rock formations. The view from the top is stunning, and you will feel like you are on top of the world.
4. Delphi: This is another UNESCO World Heritage Site, and it was considered by the ancient Greeks to be the center of the world. You can visit the Temple of Apollo and the Oracle of Delphi, among other historical landmarks.
5. Corfu Island: This island has a lot to offer, including beaches, museums, and archaeological sites. You can visit Achilleion Palace, Old Fortress and Canal d'Amour Beach.
These places are just a few of the many amazing destinations that Greece has to offer. You should definitely try the local food and drink, like souvlaki, moussaka, tzatziki and ouzo. Don't forget to interact with locals who are friendly, hospitable and always happy to help. Enjoy your stay in Greece, and don't forget to take lots of pictures!
If you have 2 weeks
Greece, what a stunning location! I am thrilled to help you plan an exciting two-week adventure.
First, I suggest exploring the ancient historical sites of Athens- visiting the Acropolis and Parthenon, along with the Agora, and the Temple of Olympian Zeus. These landmarks are not only rich in history but also offer breathtaking views of the city. You can hire a local tour guide to learn more about the fascinating past of this region.
Next, head to the beautiful island of Santorini for some awe-inspiring views of the Aegean Sea. The island is famous for its iconic white-washed buildings, blue-domed churches, and stunning sunsets. Enjoy a glass of local wine while watching the sunset over the caldera. Also, visit the red beach, Akrotiri, and Perissa beach, which offer different experiences.
After that, take a ferry to the island of Crete, known for its vast coastline and charming villages. Explore the rugged Samaria Gorge or relax on the pristine beaches of Elafonisi and Balos Lagoon. Also, don't miss trying the local cuisine, including dishes such as moussaka, souvlaki, feta cheese, and Greek yogurt.
Finally, wrap up your trip by heading to Meteora, home to six monasteries built atop towering rock formations. This UNESCO world heritage site is surreal and gives a glimpse of how humans have interacted with nature in a harmonious way. A guided tour will give you insights into the spiritual, cultural, and historical significance of these monasteries.
Overall, Greece has so much to offer, from the historical sites of Athens to the picturesque islands and the natural beauty of Meteora. You'll be sure to have an unforgettable two weeks in this stunning country.
Culture
The culture of Greece has evolved over thousands of years, beginning in Mycenaean Greece and continuing most notably into Classical Greece, through the influence of the Roman Empire and its Greek Eastern continuation, the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire. Other cultures and nations, such as the Latin and Frankish states, the Ottoman Empire, the Venetian Republic, the Genoese Republic, and the British Empire have also left their influence on modern Greek culture, although historians credit the Greek War of Independence with revitalising Greece and giving birth to a single, cohesive entity of its multi-faceted culture.
In ancient times, Greece was the birthplace of Western culture. Modern democracies owe a debt to Greek beliefs in government by the people, trial by jury, and equality under the law. The ancient Greeks pioneered in many fields that rely on systematic thought, including logic, biology, geometry, government, geography, medicine, history, philosophy, physics, and mathematics. They introduced such important literary forms as epic and lyrical poetry, history, tragedy, comedy and drama. In their pursuit of order and proportion, the Greeks created an ideal of beauty that strongly influenced Western art.
Artistic production in Greece began in the prehistoric pre-Greek Cycladic and the Minoan civilizations, both of which were influenced by local traditions and the art of ancient Egypt.
There were several interconnected traditions of painting in ancient Greece. Due to their technical differences, they underwent somewhat differentiated developments. Not all painting techniques are equally well represented in the archaeological record. The most respected form of art, according to authors like Pliny or Pausanias, were individual, mobile paintings on wooden boards, technically described as panel paintings. Also, the tradition of wall painting in Greece goes back at least to the Minoan and Mycenaean Bronze Age, with the lavish fresco decoration of sites like Knossos, Tiryns and Mycenae. Much of the figural or architectural sculpture of ancient Greece was painted colourfully. This aspect of Greek stonework is described as polychrome.
Ancient Greek sculpture was composed almost entirely of marble or bronze; with cast bronze becoming the favoured medium for major works by the early 5th century. Both marble and bronze are easy to form and very durable. Chryselephantine sculptures, used for temple cult images and luxury works, used gold, most often in leaf form and ivory for all or parts (faces and hands) of the figure, and probably gems and other materials, but were much less common, and only fragments have survived. By the early 19th century, the systematic excavation of ancient Greek sites had brought forth a plethora of sculptures with traces of notably multicolored surfaces. It was not until published findings by German archaeologist Vinzenz Brinkmann in the late 20th century, that the painting of ancient Greek sculptures became an established fact.
The art production continued also during the Byzantine era. The most salient feature of this new aesthetic was its "abstract", or anti-naturalistic character. If classical art was marked by the attempt to create representations that mimicked reality as closely as possible, Byzantine art seems to have abandoned this attempt in favour of a more symbolic approach. The Byzantine painting concentrated mainly on icons and hagiographies. The Macedonian art (Byzantine) was the artistic expression of Macedonian Renaissance, a label sometimes used to describe the period of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire (867–1056), especially the 10th century, which some scholars have seen as a time of increased interest in classical scholarship and the assimilation of classical motifs into Christian artwork.
Post Byzantine art schools include the Cretan School and Heptanese School. The first artistic movement in the Greek Kingdom can be considered the Greek academic art of the 19th century (Munich School). Notable modern Greek painters include Nikolaos Gyzis, Georgios Jakobides, Theodoros Vryzakis, Nikiforos Lytras, Konstantinos Volanakis, Nikos Engonopoulos and Yannis Tsarouchis, while some notable sculptors are Pavlos Prosalentis, Ioannis Kossos, Leonidas Drosis, Georgios Bonanos and Yannoulis Chalepas.
The architecture of ancient Greece was produced by the ancient Greeks (Hellenes), whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Aegean Islands and their colonies, for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC. The formal vocabulary of ancient Greek architecture, in particular the division of architectural style into three defined orders: the Doric Order, the Ionic Order and the Corinthian Order, was to have profound effect on Western architecture of later periods.
Byzantine architecture is the architecture promoted by the Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, which dominated Greece and the Greek speaking world during the Middle Ages. The empire endured for more than a millennium, dramatically influencing Medieval architecture throughout Europe and the Near East, and becoming the primary progenitor of the Renaissance and Ottoman architectural traditions that followed its collapse.
After the Greek Independence, the modern Greek architects tried to combine traditional Greek and Byzantine elements and motives with the western European movements and styles. Patras was the first city of the modern Greek state to develop a city plan. In January 1829, Stamatis Voulgaris, a Greek engineer of the French army, presented the plan of the new city to the Governor Kapodistrias, who approved it. Voulgaris applied the orthogonal rule in the urban complex of Patras.
Two special genres can be considered the Cycladic architecture, featuring white-coloured houses, in the Cyclades and the Epirotic architecture in the region of Epirus. Important is also the influence of the Venetian style in the Ionian islands and the "Mediterranean style" of Florestano Di Fausto (during the years of the fascist regime) in the Dodecanese islands.
After the establishment of the Greek Kingdom, the architecture of Athens and other cities was mostly influenced by the Neoclassical architecture. For Athens, the first King of Greece, Otto of Greece, commissioned the architects Stamatios Kleanthis and Eduard Schaubert to design a modern city plan fit for the capital of a state. As for Thessaloniki, after the fire of 1917, the government ordered for a new city plan under the supervision of Ernest Hébrard. Other modern Greek architects include Anastasios Metaxas, Lysandros Kaftanzoglou, Panagis Kalkos, Ernst Ziller, Xenophon Paionidis, Dimitris Pikionis and Georges Candilis.
There is an emerging need to secure the long-term preservation of the archaeological sites and monuments of Greece against the growing threats of climate change.
Theatre in its western form was born in Greece. The city-state of Classical Athens, which became a significant cultural, political, and military power during this period, was its centre, where it was institutionalised as part of a festival called the Dionysia, which honoured the god Dionysus. Tragedy (late 6th century BC), comedy (486 BC), and the satyr play were the three dramatic genres to emerge there.
During the Byzantine period, the theatrical art was heavily declined. According to Marios Ploritis, the only form survived was the folk theatre (Mimos and Pantomimos), despite the hostility of the official state. Later, during the Ottoman period, the main theatrical folk art was the Karagiozis. The renaissance which led to the modern Greek theatre, took place in the Venetian Crete. Significal dramatists include Vitsentzos Kornaros and Georgios Chortatzis.
The modern Greek theatre was born after the Greek independence, in the early 19th century, and initially was influenced by the Heptanesean theatre and melodrama, such as the Italian opera. The Nobile Teatro di San Giacomo di Corfù was the first theatre and opera house of modern Greece and the place where the first Greek opera, Spyridon Xyndas' The Parliamentary Candidate (based on an exclusively Greek libretto) was performed. During the late 19th and early 20th century, the Athenian theatre scene was dominated by revues, musical comedies, operettas and nocturnes and notable playwrights included Spyridon Samaras, Dionysios Lavrangas, Theophrastos Sakellaridis and others.
The National Theatre of Greece was opened in 1900 as Royal Theatre. Notable playwrights of the modern Greek theatre include Gregorios Xenopoulos, Nikos Kazantzakis, Pantelis Horn, Alekos Sakellarios and Iakovos Kambanelis, while notable actors include Cybele Andrianou, Marika Kotopouli, Aimilios Veakis, Orestis Makris, Katina Paxinou, Manos Katrakis and Dimitris Horn. Significant directors include Dimitris Rontiris, Alexis Minotis and Karolos Koun.
Greek literature can be divided into three main categories: Ancient, Byzantine and modern Greek literature.
Athens is considered the birthplace of Western literature. At the beginning of Greek literature stand the two monumental works of Homer: the Iliad and the Odyssey. Though dates of composition vary, these works were fixed around 800 BC or after. In the classical period many of the genres of western literature became more prominent. Lyrical poetry, odes, pastorals, elegies, epigrams; dramatic presentations of comedy and tragedy; historiography, rhetorical treatises, philosophical dialectics, and philosophical treatises all arose in this period. The two major lyrical poets were Sappho and Pindar. The Classical era also saw the dawn of drama.
Of the hundreds of tragedies written and performed during the classical age, only a limited number of plays by three authors have survived: those of Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides. The surviving plays by Aristophanes are also a treasure trove of comic presentation, while Herodotus and Thucydides are two of the most influential historians in this period. The greatest prose achievement of the 4th century was in philosophy with the works of the three great philosophers.
Byzantine literature refers to literature of the Byzantine Empire written in Atticizing, Medieval and early Modern Greek, and it is the expression of the intellectual life of the Byzantine Greeks during the Christian Middle Ages. Although popular Byzantine literature and early Modern Greek literature both began in the 11th century, the two are indistinguishable.
Modern Greek literature refers to literature written in common Modern Greek, emerging from late Byzantine times in the 11th century. The Cretan Renaissance poem Erotokritos is considered the masterpiece of this period of Greek literature. It is a verse romance written around 1600 by Vitsentzos Kornaros (1553–1613). Later, during the period of Greek enlightenment (Diafotismos), writers such as Adamantios Korais and Rigas Feraios prepared with their works the Greek Revolution (1821–1830).
Leading figures of modern Greek literature include Dionysios Solomos, Andreas Kalvos, Angelos Sikelianos, Emmanuel Rhoides, Demetrius Vikelas, Kostis Palamas, Penelope Delta, Yannis Ritsos, Alexandros Papadiamantis, Nikos Kazantzakis, Andreas Embeirikos, Kostas Karyotakis, Gregorios Xenopoulos, Constantine P. Cavafy, Nikos Kavvadias, Kostas Varnalis and Kiki Dimoula. Two Greek authors have been awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature: George Seferis in 1963 and Odysseas Elytis in 1979.
Most western philosophical traditions began in Ancient Greece in the 6th century BC. The first philosophers are called "Presocratics", which designates that they came before Socrates, whose contributions mark a turning point in western thought. The Presocratics were from the western or the eastern colonies of Greece and only fragments of their original writings survive, in some cases merely a single sentence.
A new period of philosophy started with Socrates. Like the Sophists, he rejected entirely the physical speculations in which his predecessors had indulged, and made the thoughts and opinions of people his starting-point. Aspects of Socrates were first united from Plato, who also combined with them many of the principles established by earlier philosophers, and developed the whole of this material into the unity of a comprehensive system.
Aristotle of Stagira, the most important disciple of Plato, shared with his teacher the title of the greatest philosopher of antiquity. But while Plato had sought to elucidate and explain things from the supra-sensual standpoint of the forms, his pupil preferred to start from the facts given to us by experience. Except from these three most significant Greek philosophers other known schools of Greek philosophy from other founders during ancient times were Stoicism, Epicureanism, Skepticism and Neoplatonism.
Byzantine philosophy refers to the distinctive philosophical ideas of the philosophers and scholars of the Byzantine Empire, especially between the 8th and 15th centuries. It was characterised by a Christian world-view, but one which could draw ideas directly from the Greek texts of Plato, Aristotle, and the Neoplatonists.
On the eve of the Fall of Constantinople, Gemistus Pletho tried to restore the use of the term "Hellene" and advocated the return to the Olympian Gods of the ancient world. After 1453 a number of Greek Byzantine scholars who fled to western Europe contributed to the Renaissance.
In modern period, Diafotismos (Greek: Διαφωτισμός, "enlightenment", "illumination") was the Greek expression of the Age of Enlightenment and its philosophical and political ideas. Some notable representatives were Adamantios Korais, Rigas Feraios and Theophilos Kairis.
Other modern era Greek philosophers or political scientists include Cornelius Castoriadis, Nicos Poulantzas and Christos Yannaras.
Greek vocal music extends far back into ancient times where mixed-gender choruses performed for entertainment, celebration and spiritual reasons. Instruments during that period included the double-reed aulos and the plucked string instrument, the lyre, especially the special kind called a kithara. Music played an important role in the education system during ancient times. Boys were taught music from the age of six. Later influences from the Roman Empire, Middle East, and the Byzantine Empire also had effect on Greek music.
While the new technique of polyphony was developing in the West, the Eastern Orthodox Church resisted any type of change. Therefore, Byzantine music remained monophonic and without any form of instrumental accompaniment. As a result, and despite certain attempts by certain Greek chanters (such as Manouel Gazis, Ioannis Plousiadinos or the Cypriot Ieronimos o Tragoudistis), Byzantine music was deprived of elements of which in the West encouraged an unimpeded development of art. However, this method which kept music away from polyphony, along with centuries of continuous culture, enabled monophonic music to develop to the greatest heights of perfection. Byzantium presented the monophonic Byzantine chant; a melodic treasury of inestimable value for its rhythmical variety and expressive power.
Along with the Byzantine (Church) chant and music, the Greek people also cultivated the Greek folk song (Demotiko) which is divided into two cycles, the akritic and klephtic. The akritic was created between the 9th and 10th centuries and expressed the life and struggles of the akrites (frontier guards) of the Byzantine empire, the most well known being the stories associated with Digenes Akritas. The klephtic cycle came into being between the late Byzantine period and the start of the Greek War of Independence. The klephtic cycle, together with historical songs, paraloghes (narrative song or ballad), love songs, mantinades, wedding songs, songs of exile and dirges express the life of the Greeks. There is a unity between the Greek people's struggles for freedom, their joys and sorrow and attitudes towards love and death.
The Heptanesean kantádhes (καντάδες 'serenades'; sing.: καντάδα) became the forerunners of the Greek modern urban popular song, influencing its development to a considerable degree. For the first part of the next century, several Greek composers continued to borrow elements from the Heptanesean style. The most successful songs during the period 1870–1930 were the so-called Athenian serenades, and the songs performed on stage (επιθεωρησιακά τραγούδια 'theatrical revue songs') in revue, operettas and nocturnes that were dominating Athens' theater scene.
Rebetiko, initially a music associated with the lower classes, later (and especially after the population exchange between Greece and Turkey) reached greater general acceptance as the rough edges of its overt subcultural character were softened and polished, sometimes to the point of unrecognizability. It was the base of the later laïkó (song of the people). The leading performers of the genre include Vassilis Tsitsanis, Grigoris Bithikotsis, Stelios Kazantzidis, George Dalaras, Haris Alexiou and Glykeria.
Regarding the classical music, it was through the Ionian islands (which were under western rule and influence) that all the major advances of the western European classical music were introduced to mainland Greeks. The region is notable for the birth of the first School of modern Greek classical music (Heptanesean or Ionian School, Greek: Επτανησιακή Σχολή), established in 1815. Prominent representatives of this genre include Nikolaos Mantzaros, Spyridon Xyndas, Spyridon Samaras and Pavlos Carrer. Manolis Kalomiris is considered the founder of the Greek National School of Music.
In the 20th century, Greek composers have had a significant impact on the development of avant garde and modern classical music, with figures such as Iannis Xenakis, Nikos Skalkottas, and Dimitri Mitropoulos achieving international prominence. At the same time, composers and musicians such as Mikis Theodorakis, Manos Hatzidakis, Eleni Karaindrou, Vangelis and Demis Roussos garnered an international following for their music, which include famous film scores such as Zorba the Greek, Serpico, Never on Sunday, America America, Eternity and a Day, Chariots of Fire, Blade Runner, among others. Greek American composers known for their film scores include also Yanni and Basil Poledouris. Notable Greek opera singers and classical musicians of the 20th and 21st century include Maria Callas, Nana Mouskouri, Mario Frangoulis, Leonidas Kavakos, Dimitris Sgouros and others.
During the dictatorship of the Colonels, the music of Mikis Theodorakis was banned by the junta and the composer was jailed, internally exiled, and put in a concentration camp, before finally being allowed to leave Greece due to international reaction to his detention. Released during the junta years, Anthrope Agapa, ti Fotia Stamata (Make Love, Stop the Gunfire), by the pop group Poll is considered the first anti-war protest song in the history of Greek rock. The song was echoing the hippie slogan Make love, not war and was inspired directly by the Vietnam War, becoming a "smash hit" in Greece.
Greece participated in the Eurovision Song Contest 35 times after its debut at the 1974 Contest. In 2005, Greece won with the song "My Number One", performed by Greek-Swedish singer Elena Paparizou. The song received 230 points with 10 sets of 12 points from Belgium, Bulgaria, Hungary, the United Kingdom, Turkey, Albania, Cyprus, Serbia & Montenegro, Sweden and Germany and also became a smash hit in different countries and especially in Greece. The 51st Eurovision Song Contest was held in Athens at the Olympic Indoor Hall of the Athens Olympic Sports Complex in Maroussi, with hosted by Maria Menounos and Sakis Rouvas.
Greek cuisine is characteristic of the Mediterranean diet, which is epitomised by dishes of Crete. Greek cuisine incorporates fresh ingredients into a variety of local dishes such as moussaka, pastitsio, classic Greek salad, fasolada, spanakopita and souvlaki. Some dishes can be traced back to ancient Greece like skordalia (a thick purée of walnuts, almonds, crushed garlic and olive oil), lentil soup, retsina (white or rosé wine sealed with pine resin) and pasteli (candy bar with sesame seeds baked with honey). Throughout Greece people often enjoy eating from small dishes such as meze with various dips such as tzatziki, grilled octopus and small fish, feta cheese, dolmades (rice, currants and pine kernels wrapped in vine leaves), various pulses, olives and cheese. Olive oil is added to almost every dish.
Some sweet desserts include melomakarona, diples and galaktoboureko, and drinks such as ouzo, metaxa and a variety of wines including retsina. Greek cuisine differs widely from different parts of the mainland and from island to island. It uses some flavorings more often than other Mediterranean cuisines: oregano, mint, garlic, onion, dill and bay laurel leaves. Other common herbs and spices include basil, thyme and fennel seed. Many Greek recipes, especially in the northern parts of the country, use "sweet" spices in combination with meat, for example cinnamon and cloves in stews.
Koutoukia are an underground restaurant common in Greece.
Cinema first appeared in Greece in 1896, but the first actual cine-theatre was opened in 1907 in Athens. In 1914, the Asty Films Company was founded and the production of long films began. Golfo (Γκόλφω), a well known traditional love story, is considered the first Greek feature film, although there were several minor productions such as newscasts before this. In 1931, Orestis Laskos directed Daphnis and Chloe (Δάφνις και Χλόη), containing one of the first nude scene in the history of European cinema; it was also the first Greek movie which was played abroad. In 1944, Katina Paxinou was honoured with the Best Supporting Actress Academy Award for For Whom the Bell Tolls.
The 1950s and early 1960s are considered by many to be a "golden age" of Greek cinema. Directors and actors of this era were recognised as important figures in Greece and some gained international acclaim: George Tzavellas, Irene Papas, Melina Mercouri, Michael Cacoyannis, Alekos Sakellarios, Nikos Tsiforos, Iakovos Kambanelis, Katina Paxinou, Nikos Koundouros, Ellie Lambeti and others. More than sixty films per year were made, with the majority having film noir elements. Some notable films include The Drunkard (1950, directed by George Tzavellas), The Counterfeit Coin (1955, by Giorgos Tzavellas), Πικρό Ψωμί (1951, by Grigoris Grigoriou), O Drakos (1956, by Nikos Koundouros), Stella (1955, directed by Cacoyannis and written by Kampanellis), Woe to the Young (1961, by Alekos Sakellarios), Glory Sky (1962, by Takis Kanellopoulos) and The Red Lanterns (1963, by Vasilis Georgiadis)
Cacoyannis also directed Zorba the Greek with Anthony Quinn which received Best Director, Best Adapted Screenplay and Best Film nominations. Finos Film also contributed in this period with movies such as Λατέρνα, Φτώχεια και Φιλότιμο, Madalena, I theia ap' to Chicago, Το ξύλο βγήκε από τον Παράδεισο and many more.
During the 1970s and 1980s, Theo Angelopoulos directed a series of notable and appreciated movies. His film Eternity and a Day won the Palme d'Or and the Prize of the Ecumenical Jury at the 1998 Cannes Film Festival.
There are also internationally renowned filmmakers in the Greek diaspora, such as the Greek-French Costa-Gavras and the Greek-Americans Elia Kazan, John Cassavetes and Alexander Payne. More recently Yorgos Lanthimos (film and stage director, producer, and screenwriter) has received four Academy Award nominations for his work, including Best Foreign Language Film for Dogtooth (2009), Best Original Screenplay for The Lobster (2015), and Best Picture and Best Director for The Favourite (2018).
Greece is the birthplace of the ancient Olympic Games, first recorded in 776 BC in Olympia, and hosted the modern Olympic Games twice, the inaugural 1896 Summer Olympics and the 2004 Summer Olympics. During the parade of nations, Greece is always called first, as the founding nation of the ancient precursor of modern Olympics. The nation has competed at every Summer Olympic Games, one of only four countries to have done so. Having won a total of 110 medals (30 gold, 42 silver and 38 bronze), Greece is ranked 32nd by gold medals in the all-time Summer Olympic medal count. Their best ever performance was in the 1896 Summer Olympics, when Greece finished second in the medal table with 10 gold medals.
The Greece national football team, ranking 12th in the world in 2014 (and having reached a high of 8th in the world in 2008 and 2011), were crowned European Champions in Euro 2004 in one of the biggest upsets in the history of the sport. The Greek Super League is the highest professional football league in the country, comprising fourteen teams. The most successful are Olympiacos, Panathinaikos, and AEK Athens.
The Greek national basketball team has a decades-long tradition of excellence in the sport, being considered among the world's top basketball powers. , it ranked 4th in the world and 2nd in Europe. They have won the European Championship twice in 1987 and 2005, and have reached the final four in two of the last four FIBA World Championships, taking the second place in the world in 2006 FIBA World Championship, after a 101–95 win against Team US in the tournament's semi-final. The domestic top basketball league, A1 Ethniki, is composed of fourteen teams. The most successful Greek teams are Panathinaikos, Olympiacos, Aris Thessaloniki, AEK Athens and P.A.O.K. Greek basketball teams are the most successful in European basketball the last 25 years, having won 9 Euroleagues since the establishment of the modern era Euroleague Final Four format in 1988, while no other nation has won more than 4 Euroleague championships in this period. Besides the 9 Euroleagues, Greek basketball teams (Panathinaikos, Olympiacos, Aris Thessaloniki, AEK Athens, P.A.O.K, Maroussi) have won 3 Triple Crowns, 5 Saporta Cups, 2 Korać Cups and 1 FIBA Europe Champions Cup. After the 2005 European Championship triumph of the Greek national basketball team, Greece became the reigning European Champion in both football and basketball.
The Greece women's national water polo team have emerged as one of the leading powers in the world, becoming World Champions after their gold medal win against the hosts China at the 2011 World Championship. They also won the silver medal at the 2004 Summer Olympics, the gold medal at the 2005 World League and the silver medals at the 2010 and 2012 European Championships. The Greece men's national water polo team became the third best water polo team in the world in 2005, after their win against Croatia in the bronze medal game at the 2005 World Aquatics Championships in Canada. The domestic top water polo leagues, Greek Men's Water Polo League and Greek Women's Water Polo League are considered amongst the top national leagues in European water polo, as its clubs have made significant success in European competitions. In men's European competitions, Olympiacos has won the Champions League, the European Super Cup and the Triple Crown in 2002 becoming the first club in water polo history to win every title in which it has competed within a single year (National championship, National cup, Champions League and European Super Cup), while NC Vouliagmeni has won the LEN Cup Winners' Cup in 1997. In women's European competitions, Greek water polo teams (NC Vouliagmeni, Glyfada NSC, Olympiacos, Ethnikos Piraeus) are amongst the most successful in European water polο, having won 4 LEN Champions Cups, 3 LEN Trophies and 2 European Supercups.
The Greek men's national volleyball team has won two bronze medals, one in the European Volleyball Championship and another one in the Men's European Volleyball League, a 5th place in the Olympic Games and a 6th place in the FIVB Volleyball Men's World Championship. The Greek league, the A1 Ethniki, is considered one of the top volleyball leagues in Europe and the Greek clubs have had significant success in European competitions. Olympiacos is the most successful volleyball club in the country having won the most domestic titles and being the only Greek club to have won European titles; they have won two CEV Cups, they have been CEV Champions League runners-up twice and they have played in 12 Final Fours in the European competitions, making them one of the most traditional volleyball clubs in Europe. Iraklis have also seen significant success in European competitions, having been three times runners-up of the CEV Champions League.
In handball, AC Diomidis Argous is the only Greek club to have won a European Cup.
Apart from these, cricket is relatively popular in Corfu.
The numerous gods of the ancient Greek religion as well as the mythical heroes and events of the ancient Greek epics (The Odyssey and The Iliad) and other pieces of art and literature from the time make up what is nowadays colloquially referred to as Greek mythology. Apart from serving a religious function, the mythology of the ancient Greek world also served a cosmological role as it was meant to try to explain how the world was formed and operated.
The principal gods of the ancient Greek religion were the Dodekatheon, or the Twelve Gods, who lived on the top of Mount Olympus. The most important of all ancient Greek gods was Zeus, the king of the gods, who was married to his sister, Hera. The other Greek gods that made up the Twelve Olympians were Ares, Poseidon, Athena, Demeter, Dionysus, Apollo, Artemis, Aphrodite, Hephaestus, and Hermes. Despite her humble status within the hierarchy of the Olympians, Hestia, the goddess of the hearth and sacred flame, was likely the most prayed to of all gods. It is believed that essentially all home offering ceremonies and most public festival offerings began and ended with an invocation and offering to Hestia. Apart from these 13 gods, the Greek pantheon was filled with dozens of other gods, demigods, and mortal and immortal beings which varied by local and over the evolution of Greek culture. A variety of other mystical beliefs and nature spirits such as nymphs and other magical creatures were foundational to the ancient Greek understanding of the world around them.
According to Greek law, every Sunday of the year is a public holiday. Since the late '70s, Saturday also is a non-school and not working day. In addition, there are four mandatory official public holidays: 25 March (Greek Independence Day), Easter Monday, 15 August (Assumption or Dormition of the Holy Virgin), and 25 December (Christmas). 1 May (Labour Day) and 28 October (Ohi Day) are regulated by law as being optional but it is customary for employees to be given the day off. There are, however, more public holidays celebrated in Greece than are announced by the Ministry of Labour each year as either obligatory or optional. The list of these non-fixed national holidays rarely changes and has not changed in recent decades, giving a total of eleven national holidays each year.
In addition to the national holidays, there are public holidays that are not celebrated nationwide, but only by a specific professional group or a local community. For example, many municipalities have a "Patron Saint" parallel to "Name Days", or a "Liberation Day". On such days it is customary for schools to take the day off.
Notable festivals, beyond the religious fests, include Patras Carnival, Athens Festival and various local wine festivals. The city of Thessaloniki is also home of a number of festivals and events. The Thessaloniki International Film Festival is one of the most important film festivals in Southern Europe.
Religion
The Greek Constitution recognises Eastern Orthodoxy as the 'prevailing' faith of the country, while guaranteeing freedom of religious belief for all. The Greek government does not keep statistics on religious groups and censuses do not ask for religious affiliation. According to the U.S. State Department, an estimated 97% of Greek citizens identify themselves as Eastern Orthodox, belonging to the Greek Orthodox Church, which uses the Byzantine rite and the Greek language, the original language of the New Testament. The administration of the Greek territory is shared between the Church of Greece and the Patriarchate of Constantinople.
In a 2010 Eurostat–Eurobarometer poll, 79% of Greek citizens responded that they "believe there is a God". According to other sources, 15.8% of Greeks describe themselves as "very religious", which is the highest among all European countries. The survey also found that just 3.5% never attend a church, compared to 4.9% in Poland and 59.1% in the Czech Republic. Estimates of the recognised Greek Muslim minority, which is mostly located in Thrace, range around 100,000, (about 1% of the population). Some of the Albanian immigrants to Greece come from a nominally Muslim background, although most are secular in orientation. Following the 1919–1922 Greco-Turkish War and the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne, Greece and Turkey agreed to a population transfer based on cultural and religious identity. About 500,000 Muslims from Greece, predominantly those defined as Turks, but also Greek Muslims like the Vallahades of western Macedonia, were exchanged with approximately 1.5 million Greeks from Turkey. However, many refugees who settled in former Ottoman Muslim villages in Central Macedonia, and were defined as Christian Orthodox Caucasus Greeks, arrived from the former Russian Transcaucasus province of Kars Oblast, after it had been retroceded to Turkey prior to the official population exchange.
Judaism has been present in Greece for more than 2,000 years. The ancient community of Greek Jews are called Romaniotes, while the Sephardi Jews were once a prominent community in the city of Thessaloniki, numbering some 80,000, or more than half of the population, by 1900. However, after the German occupation of Greece and the Holocaust during World War II, is estimated to number around 5,500 people.
The Roman Catholic community is estimated to be around 250,000 of which 50,000 are Greek citizens. Their community is nominally separate from the smaller Greek Byzantine Catholic Church, which recognises the primacy of the Pope but maintains the liturgy of the Byzantine Rite. Old Calendarists account for 500,000 followers. Protestants, including the Greek Evangelical Church and Free Evangelical Churches, stand at about 30,000. Other Christian minorities, such as Assemblies of God, International Church of the Foursquare Gospel and various Pentecostal churches of the Greek Synod of Apostolic Church total about 12,000 members. The independent Free Apostolic Church of Pentecost is the biggest Protestant denomination in Greece with 120 churches. There are no official statistics about Free Apostolic Church of Pentecost, but the Orthodox Church estimates the followers as 20,000. The Jehovah's Witnesses report having 28,874 active members.
Since 2017, Hellenic Polytheism, or Hellenism has been legally recognised as an actively practised religion in Greece, with estimates of 2,000 active practitioners and an additional 100,000 "sympathisers". Hellenism refers to various religious movements that continue, revive, or reconstruct ancient Greek religious practices.
Demographics
According to the official statistical body of Greece, the Hellenic Statistical Authority (ELSTAT), the country's total population in 2021 was 10,482,487. Eurostat places the current population at 10.6 million in 2022.
Greek society has changed rapidly over the last several decades, coinciding with the wider European trend of declining fertility and rapid aging. The birth rate in 2003 stood at 9.5 per 1,000 inhabitants, significantly lower than the rate of 14.5 per 1,000 in 1981. At the same time, the mortality rate increased slightly from 8.9 per 1,000 inhabitants in 1981 to 9.6 per 1,000 inhabitants in 2003. Estimates from 2016 show the birth rate decreasing further still to 8.5 per 1,000 and mortality climbing to 11.2 per 1,000.
The fertility rate of 1.41 children per woman is well below the replacement rate of 2.1, and is one of the lowest in the world, considerably below the high of 5.47 children born per woman in 1900. Subsequently, Greece's median age is 44.2 years, the seventh-highest in the world. In 2001, 16.71 percent of the population were 65 years old and older, 68.12 percent between the ages of 15 and 64 years old, and 15.18 percent were 14 years old and younger. By 2016, the proportion of the population age 65 and older had risen to 20.68 percent, while the proportion of those aged 14 and younger declined to slightly below 14 percent.
Marriage rates began declining from almost 71 per 1,000 inhabitants in 1981 until 2002, only to increase slightly in 2003 to 61 per 1,000 and then fall again to 51 in 2004. Divorce rates have seen an increase from 191.2 per 1,000 marriages in 1991 to 239.5 per 1,000 marriages in 2004.
As a result of these trends, the average Greek household is smaller and older than in previous generations. The economic crisis has exacerbated this development, with 350,000–450,000 Greeks, predominantly young adults, emigrating since 2010.
Almost two-thirds of the Greek people live in urban areas. Greece's largest and most influential metropolitan centres are those of Athens (population 3,744,059 according to 2021 census) and Thessaloniki (population 1,092,919 in 2021) that latter commonly referred to as the (συμπρωτεύουσα, ). Other prominent cities with urban populations above 100,000 inhabitants include Patras, Heraklion, Larissa, Volos, Rhodes, Ioannina, Agrinio, Chania, and Chalcis.
The table below lists the largest cities in Greece, by population contained in their respective contiguous built up urban areas, which are either made up of many municipalities, evident in the cases of Athens and Thessaloniki, or are contained within a larger single municipality, case evident in most of the smaller cities of the country. The results come from the preliminary figures of the population census that took place in Greece in May 2011.
The Greek Constitution recognises Eastern Orthodoxy as the 'prevailing' faith of the country, while guaranteeing freedom of religious belief for all. The Greek government does not keep statistics on religious groups and censuses do not ask for religious affiliation. According to the U.S. State Department, an estimated 97% of Greek citizens identify themselves as Eastern Orthodox, belonging to the Greek Orthodox Church, which uses the Byzantine rite and the Greek language, the original language of the New Testament. The administration of the Greek territory is shared between the Church of Greece and the Patriarchate of Constantinople.
In a 2010 Eurostat–Eurobarometer poll, 79% of Greek citizens responded that they "believe there is a God". According to other sources, 15.8% of Greeks describe themselves as "very religious", which is the highest among all European countries. The survey also found that just 3.5% never attend a church, compared to 4.9% in Poland and 59.1% in the Czech Republic. Estimates of the recognised Greek Muslim minority, which is mostly located in Thrace, range around 100,000, (about 1% of the population). Some of the Albanian immigrants to Greece come from a nominally Muslim background, although most are secular in orientation. Following the 1919–1922 Greco-Turkish War and the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne, Greece and Turkey agreed to a population transfer based on cultural and religious identity. About 500,000 Muslims from Greece, predominantly those defined as Turks, but also Greek Muslims like the Vallahades of western Macedonia, were exchanged with approximately 1.5 million Greeks from Turkey. However, many refugees who settled in former Ottoman Muslim villages in Central Macedonia, and were defined as Christian Orthodox Caucasus Greeks, arrived from the former Russian Transcaucasus province of Kars Oblast, after it had been retroceded to Turkey prior to the official population exchange.
Judaism has been present in Greece for more than 2,000 years. The ancient community of Greek Jews are called Romaniotes, while the Sephardi Jews were once a prominent community in the city of Thessaloniki, numbering some 80,000, or more than half of the population, by 1900. However, after the German occupation of Greece and the Holocaust during World War II, is estimated to number around 5,500 people.
The Roman Catholic community is estimated to be around 250,000 of which 50,000 are Greek citizens. Their community is nominally separate from the smaller Greek Byzantine Catholic Church, which recognises the primacy of the Pope but maintains the liturgy of the Byzantine Rite. Old Calendarists account for 500,000 followers. Protestants, including the Greek Evangelical Church and Free Evangelical Churches, stand at about 30,000. Other Christian minorities, such as Assemblies of God, International Church of the Foursquare Gospel and various Pentecostal churches of the Greek Synod of Apostolic Church total about 12,000 members. The independent Free Apostolic Church of Pentecost is the biggest Protestant denomination in Greece with 120 churches. There are no official statistics about Free Apostolic Church of Pentecost, but the Orthodox Church estimates the followers as 20,000. The Jehovah's Witnesses report having 28,874 active members.
Since 2017, Hellenic Polytheism, or Hellenism has been legally recognised as an actively practised religion in Greece, with estimates of 2,000 active practitioners and an additional 100,000 "sympathisers". Hellenism refers to various religious movements that continue, revive, or reconstruct ancient Greek religious practices.
Greece is today relatively homogeneous in linguistic terms, with a large majority of the native population using Greek as their first or only language. Among the Greek-speaking population, speakers of the distinctive Pontic dialect came to Greece from Asia Minor after the Greek genocide and constitute a sizable group. The Cappadocian dialect came to Greece due to the genocide as well, but is endangered and is barely spoken now. Indigenous Greek dialects include the archaic Greek spoken by the Sarakatsani, traditionally transhument mountain shepherds of Greek Macedonia and other parts of Northern Greece. The Tsakonian language, a distinct Greek language deriving from Doric Greek instead of Koine Greek, is still spoken in some villages in the southeastern Peloponnese.
The Muslim minority in Thrace, which amounts to approximately 0.95% of the total population, consists of speakers of Turkish, Bulgarian (Pomaks) and Romani. Romani is also spoken by Christian Roma in other parts of the country. Further minority languages have traditionally been spoken by regional population groups in various parts of the country. Their use has decreased radically in the course of the 20th century through assimilation with the Greek-speaking majority. Today they are only maintained by the older generations and are on the verge of extinction. The same goes for the Arvanites, an Albanian-speaking group mostly located in the rural areas around the capital Athens, and for the Aromanians and Megleno-Romanians, also known as "Vlachs", whose language is closely related to Romanian and who used to live scattered across several areas of mountainous central Greece. Members of these groups usually identify ethnically as Greek and are today all at least bilingual in Greek.
Near the northern Greek borders there are also some Slavic–speaking groups, locally known as Slavomacedonian-speaking, most of whose members identify ethnically as Greeks. It is estimated that after the population exchanges of 1923, Macedonia had 200,000 to 400,000 Slavic speakers. The Jewish community in Greece traditionally spoke Ladino (Judeo-Spanish), today maintained only by a few thousand speakers. Other notable minority languages include Armenian, Georgian, and the Greco-Turkic dialect spoken by the Urums, a community of Caucasus Greeks from the Tsalka region of central Georgia and ethnic Greeks from southeastern Ukraine who arrived in mainly Northern Greece as economic migrants in the 1990s.
Throughout the 20th century, millions of Greeks migrated to the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, and Germany, creating a large Greek diaspora. Net migration started to show positive numbers from the 1970s, but until the beginning of the 1990s, the main influx was that of returning Greek migrants or of Pontic Greeks and others from Russia, Georgia, Turkey the Czech Republic, and elsewhere in the former Soviet Bloc.
A study from the Mediterranean Migration Observatory maintains that the 2001 census recorded 762,191 persons residing in Greece without Greek citizenship, constituting around 7% of the total population. Of the non-citizen residents, 48,560 were EU or European Free Trade Association nationals and 17,426 were Cypriots with privileged status. The majority come from Eastern European countries: Albania (56%), Bulgaria (5%) and Romania (3%), while migrants from the former Soviet Union (Georgia, Russia, Ukraine, Moldova, etc.) comprise 10% of the total. Some of the immigrants from Albania are from the Greek minority in Albania centred on the region of Northern Epirus. In addition, the total Albanian national population which includes temporary migrants and undocumented persons is around 600,000.
The 2011 census recorded 9,903,268 Greek citizens (91.56%), 480,824 Albanian citizens (4.44%), 75,915 Bulgarian citizens (0.7%), 46,523 Romanian citizenship (0.43%), 34,177 Pakistani citizens (0.32%), 27,400 Georgian citizens (0.25%) and 247,090 people had other or unidentified citizenship (2.3%). 189,000 people of the total population of Albanian citizens were reported in 2008 as ethnic Greeks from Southern Albania, in the historical region of Northern Epirus.
The greatest cluster of non-EU immigrant population are the larger urban centers, especially the Municipality of Athens, with 132,000 immigrants comprising 17% of the local population, and then Thessaloniki, with 27,000 immigrants reaching 7% of the local population. There is also a considerable number of co-ethnics that came from the Greek communities of Albania and the former Soviet Union.
Greece, together with Italy and Spain, is a major entry point for illegal immigrants trying to enter the EU. Illegal immigrants entering Greece mostly do so from the border with Turkey at the Evros River and the islands of the eastern Aegean across from Turkey (mainly Lesbos, Chios, Kos, and Samos). In 2012, the majority of illegal immigrants entering Greece came from Afghanistan, followed by Pakistanis and Bangladeshis. In 2015, arrivals of refugees by sea had increased dramatically mainly due to the ongoing Syrian civil war. There were 856,723 arrivals by sea in Greece, an almost fivefold increase to the same period of 2014, of which the Syrians represent almost 45%. The majority of refugees and migrants use Greece as a transit country, while their intended destinations are northern European Nations such as Austria, Germany and Sweden.
Greeks have a long tradition of valuing and investing in paideia (education), which was upheld as one of the highest societal values in the Greek and Hellenistic world. The first European institution described as a university was founded in fifth-century Constantinople and continued operating in various incarnations until the city's fall to the Ottomans in 1453. The University of Constantinople was Christian Europe's first secular institution of higher learning, and by some measures was the world's first university.
Compulsory education in Greece comprises primary schools (Δημοτικό Σχολείο, Dimotikó Scholeio) and gymnasium (Γυμνάσιο). Nursery schools (Παιδικός σταθμός, Paidikós Stathmós) are popular but not compulsory. Kindergartens (Νηπιαγωγείο, Nipiagogeío) are now compulsory for any child above four years of age. Children start primary school aged six and remain there for six years. Attendance at gymnasia starts at age 12 and lasts for three years.
Greece's post-compulsory secondary education consists of two school types: unified upper secondary schools (Γενικό Λύκειο, Genikό Lykeiό) and technical–vocational educational schools (Τεχνικά και Επαγγελματικά Εκπαιδευτήρια, "TEE"). Post-compulsory secondary education also includes vocational training institutes (Ινστιτούτα Επαγγελματικής Κατάρτισης, "IEK") which provide a formal but unclassified level of education. As they can accept both Gymnasio (lower secondary school) and Lykeio (upper secondary school) graduates, these institutes are not classified as offering a particular level of education.
According to the Framework Law (3549/2007), Public higher education "Highest Educational Institutions" (Ανώτατα Εκπαιδευτικά Ιδρύματα, Anótata Ekpaideytiká Idrýmata, "ΑΕΙ") consists of two parallel sectors:the university sector (Universities, Polytechnics, Fine Arts Schools, the Open University) and the Technological sector (Technological Education Institutions (TEI) and the School of Pedagogic and Technological Education). There are also State Non-University Tertiary Institutes offering vocationally oriented courses of shorter duration (2 to 3 years) which operate under the authority of other Ministries. Students are admitted to these Institutes according to their performance at national level examinations taking place after completion of the third grade of Lykeio. Additionally, students over twenty-two years old may be admitted to the Hellenic Open University through a form of lottery. The Capodistrian University of Athens is the oldest university in the eastern Mediterranean.
The Greek education system also provides special kindergartens, primary, and secondary schools for people with special needs or difficulties in learning. There are also specialist gymnasia and high schools offering musical, theological, and physical education.
Seventy-two percent of Greek adults aged 25–64 have completed upper secondary education, which is slightly less than the OECD average of 74 percent. The average Greek pupil scored 458 in reading literacy, maths and science in the OECD's 2015 Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA). This score is lower than the OECD average of 486. On average, girls outperformed boys by 15 points, much more than the average OECD gap of two points.
Greece has universal health care. The system is mixed, combining a national health service with social health insurance (SHI). 2000 World Health Organization report, its health care system ranked 14th in overall performance of 191 countries surveyed. In a 2013 Save the Children report, Greece was ranked the 19th out of 176 countries for the state of mothers and newborn babies. In 2010, there were 138 hospitals with 31,000 beds, but in 2011, the Ministry of Health announced plans to decrease the number to 77 hospitals with 36,035 beds to reduce expenses and further enhance healthcare standards. However, as of 2014, there were 124 public hospitals, of which 106 were general hospitals and 18 specialised hospitals, with a total capacity of about 30,000 beds.
Greece's healthcare expenditures as a percentage of GDP were 9.6% in 2007, just above the OECD average of 9.5%. By 2015, spending declined to 8.4% of GDP (compared with the EU average of 9.5%), a decline of one-fifth since 2010. Nevertheless, the country maintains the highest doctor-to-population ratio of any OECD country and the highest doctor-to-patient ratio in the EU.
Life expectancy in Greece is among the highest in the world; a 2011 OECD report placed it at 80.3 years, above the OECD average of 79.5, while a more recent 2017 study found life expectancy in 2015 to be 81.1 years, slightly above the EU average of 80.6. The island of Icaria has the highest percentage of nonagenarians in the world; approximately 33% of islanders are 90 or older. Icaria is subsequently classified as a "Blue Zone", a region where people allegedly live longer than average and have lower rates of cancer, heart disease, or other chronic illnesses.
The 2011 OECD report showed that Greece had the largest percentage of adult daily smokers of any of the 34 OECD members. The country's obesity rate is 18.1%, which is above the OECD average of 15.1%, but considerably lower than the American rate of 27.7%. In 2008, Greece had the highest rate of perceived good health in the OECD, at 98.5%. Infant mortality, with a rate of 3.6 deaths per 1,000 live births, was below the 2007 OECD average of 4.9.
Cities:

